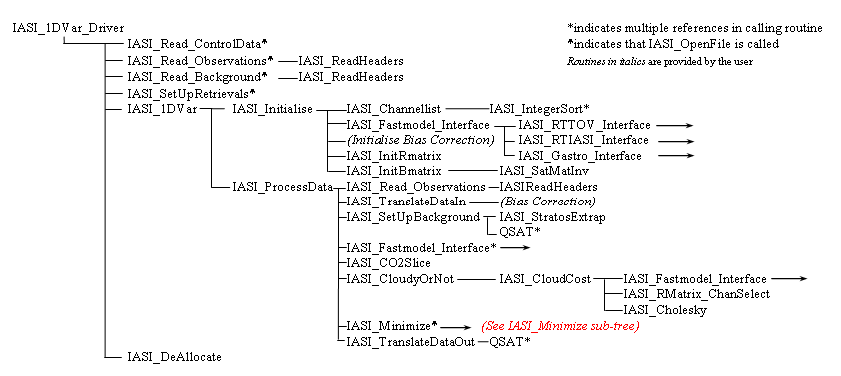
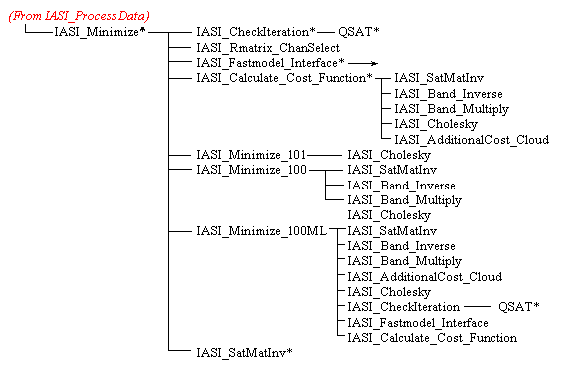
Fig. A1. IASI_1DVar Calling Tree


In addition to these subroutines, nine modules are used:
IASIMod_Channellist.f90 IASIMod_ObsInfo.f90Various structures are set up in these modules the most important of which are listed in here:
IASIMod_Constants.f90 IASIMod_Params.f90
IASIMod_CovarianceMatrices.f90 IASIMod_RTmodel.f90
| Structure | Module | Description |
| SatIDInfo_Type | IASIMod_RTmodel | This is used to define the component instruments in composite instruments such as ATOVS |
| RTParams_Type | IASIMod_RTModel | This contains profile, instrument choice and geometry information that is required by the RT model plus the radiances and Jacobians returned from the model. |
| ModelOB_Type | IASIMod_ObsInfo | This contains background information for each observations including modelled radiances |
| OB_Type | IASIMod_ObsInfo | This contains the observed radiances plus auxiliary information (e.g., latitude, longitude, surface elevation etc.). It is also used to store the retrieved profile and information on the retrieval process (e.g., final cost function). |
| R_Matrix_Type | IASIMod_Covariance_Matrices | This stores the observational error covariance matrices (in a variety of forms). |
| Channel_Selection_Type | IASIMod_Channellist | Stores the channel selection choices. |
|
IASI_1DVar_Driver This is the main driver program | |
|
Called by: < NONE > |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_Read_ControlData IASI_Read_Observations IASI_Read_Background IASI_SetUpRetrievals IASI_1DVar IASI_DeAllocate |
|
Gen_Error_Report A generic error output subroutine | |
|
Called by: Many subroutines |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_MessageReport (3 times) |
|
Gen_FreeUnit Frees a fortran I/O unit number previously assigned by Gen_GetUnit. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Initialise |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Message_Report |
|
Gen_GetUnit Supplies an unused fortran I/O unit number. | |
|
Called by: IASI_OpenFile |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Message_Report |
|
Gen_MessageReport A generic routine for outputting informational messages. | |
|
Called by: Gen_Error_Report IASI_1DVar IASI_InitBmatrix IASI_InitRmatrix IASI_Initialise IASI_OpenFile IASI_ProcessData IASI_Gastro_Interface IASI_RTIASI_Interface IASI_RTTOV7_Interface |
Calls (in order of first call): < NONE > |
|
IASI_1DVar The main calling routine for initialising and minimising the data (the main input routines have already been called). | |
|
Called by: IASI_1DVar_Driver |
Calls
(in order of first call): IASI_Initialise Gen_MessageReport (2 times) IASI_ProcessData IASI_SetUpRetrievals |
|
IASI_AdditionalCost_Cloud When performing cloudy retrievals an additional cost is added to the cost function if the cloud top pressure or cloud fraction fall outside the allowed bounds (200hPa-Surface Pressure and 0-1 respectively). The additional cost increases as the cube of the distance from the bound. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Calculate_Cost_Function IASI_Minimize_100ML |
Calls
(in order of first call): <NONE> |
|
IASI_BandInverse Invert a band diagonal, symmetric, positive definite matrix. This is used with the observational error covariance matrix. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Calculate_Cost_Function IASI_Minimize_100 IASI_Minimize_100ML |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Error_Report |
|
IASI_BandMultiply Multiply a matrix by a band diagonal matrix. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Calculate_Cost_Function IASI_Minimize_100 IASI_Minimize_100ML |
Calls (in order of first call): < NONE > |
|
IASI_Calculate_Cost_Function Evaluates the cost function and, optionally, its gradient (returned as a vector with length equal to the length of the state vector). A subroutine that calculates an additional cost term for cloud retrievals may be called when required. Note that if the Rodgers (1976) Eqn. 101 form of the minimisation is being used, the cost function is evaluated using the diagonal elements of the observational error covariance matrix only. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Minimize IASI_Minimize_100ML |
Calls (in order
of first call): IASI_SatMatInv IASI_BandInverse IASI_BandMultiply IASI_AdditionalCost_Cloud Gen_Error_Report (5 times) |
|
IASI_Channellist Reads in channels to be used in various retrieval situations. The use of each channel that is used at all is specified in the ChannelChoice.dat file through a binary code (described in the header to the file and in this subroutine). From the same file, this subroutine reads in which channels are to be used in monitoring (stored in the BackChans structure) and in cloud detection (stored in DetectCloudChans). | |
|
Called by: IASI_Initialise |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Error_Report (6 times) IASI_IntegerSort (3 times) |
|
IASI_CheckIteration Resets the profile variables to within pre-defined soft-limits (as contained in the Soft_Limits structure) and sets the Profile_Variables_Reset to true in this case. If the profile is beyond the wider predefined gross-limits, Out_of_Range is then set to true. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Minimize IASI_Minimize_100ML |
Calls (in order of first call): QSAT (2 times) |
|
IASI_CheckTemperatures A FUNCTION that checks for the input temperatures being inside gross limits. | |
|
Called by: IASI_SetUpBackground |
Calls (in order of first call): < NONE > |
|
IASI_Cholesky Solves the linear equation Uq=V for q where U is a symmetric positive definite matrix and v and q are vectors of equal length. See Golub and Van Loan (1996). If U is not positive definite this will be detected by the program and flagged as an error. U is assumed to be symmetric as only the upper triangle is in fact used. | |
|
Called by: IASI_CloudCost IASI_Minimize_100 IASI_Minimize_100ML IASI_Minimize_101 |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Error_Report |
|
IASI_CloudCost Calculates the cloudy cost function as defined in Eqn. 6 of English, Eyre and Smith (1999). | |
|
Called by: IASI_CloudyOrNot |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_Fastmodel_Interface IASI_RMatrix_ChanSelect Gen_Error_Report (2 times) IASI_Cholesky |
|
IASI_CloudyOrNot This is the cloud detection module and uses the method described by English, Eyre and Smith (1999). | |
|
Called by: IASI_ProcessData |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_CloudCost |
|
IASI_CO2Slice The CO2-slicing technique is used to obtain a better first guess of the cloud top height and fraction before the 1DVar is used to refine this guess. The cloud detection channels are used for this purpose. | |
|
Called by: IASI_ProcessData |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_ErrorReport (3 times) |
|
IASI_DeAllocate Deallocates any remaining allocated arrays before exiting the program. | |
|
Called by: IASI_1DVar_Driver |
Calls (in order of first call): < NONE > |
|
IASI_Fastmodel_Interface This is the interface routine between the main 1DVar code and the fastmodels (see IASI_RTTOV7_Interface and IASI_RTIASI_Interface for details. | |
|
Called by: IASI_CloudCost IASI_Initialise IASI_Minimize IASI_Minimize_100ML IASI_ProcessData |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_Gastro_Interface IASI_RTTOV7_Interface IASI_RTTOV8_Interface IASI_RTIASI_Interface Gen_Error_Report |
|
IASI_InitBmatrix Reads in the background error covariance matrix, cuts out any unwanted elements and calculates the inverse. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Initialise |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Error_Report (2 times) IASI_SatMatInv Gen_Message_Report |
|
IASI_InitRmatrix Reads in the observational error covariance matrices for all required instruments. There are three possible formats: 1) Full matrix representation 2) Band-diagonal representations (diagonal being a sub-set of this) 3) Eigenvalue-Eigenvector representation The error covariances are given in terms of brightness temperature and implicitly include forward modelling error. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Initialise |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Error_Report (3 times) Gen_Message_Report (4 times) |
|
IASI_Initialise This is the main initialisation routine. It starts by opening the files that are required by the program Next the IASI_Channellist routine is called which sets up the channel selection choices for various cloud and surface type scenarios. The fastmodels are initialised next throught the IASI_Fastmodel_Interface subroutine. The user may then initialise their bias correction scheme before the background and observation error covariance matrices are read in. | |
|
Called by: IASI_1DVar |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Message_Report (4 times) IASI_OpenFile (7 times) IASI_Channellist IASI_Fastmodel_Interface Gen_Error_Report (2 times) IASI_InitRmatrix IASI_InitBmatrix Gen_FreeUnit |
|
IASI_Minimize This subroutine contains the main iterative loop for minimisation. One of three minimisation algorithms are used depending on the dimensions and non-linearity of the problem (see below).
The minimisation process is iterated until the convergence
criteria are met. These are: | |
|
Called by: IASI_ProcessData |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_CheckIteration (2 times) IASI_RMatrix_ChanSelect IASI_Fastmodel_Interface (2 times) IASI_Calculate_Cost_Function (2 times) IASI_Minimize_101 IASI_Minimize_100ML IASI_Minimize_100 IASI_SatMatInv (2 times) |
|
IASI_Minimize_100 Updates the input profile vector (Delta_Profile) according to Rodgers (1976), Eqn. 100. This is the optimal equation to use for linear problems where the size of the observation vector is larger than the size of the state vector. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Minimize |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_SatMatInv IASI_BandInverse IASI_BandMultiply Gen_Error_Report (2 times) IASI_Cholesky |
|
IASI_Minimize_100ML Updates the input profile vector (Delta_Profile) according to Rodgers (1976), Eqn. 100, modified from the Gauss-Newton form to the Marquardt-Levenberg form (see Rodgers, 2000). This min imisation scheme should be used for non-linear problems where Gauss-Newton descent is inefficient. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Minimize |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_SatMatInv IASI_BandInverse IASI_BandMultiply Gen_Error_Report (2 times) IASI_Cholesky IASI_CheckIteration (2 times) IASI_Fastmodel_Interface (2 times) IASI_Calculate_Cost_Function |
|
IASI_Minimize_101 Updates the input profile vector (Delta_Profile) according to Rodgers (1976), Eqn. 101. This is the optimal equation to use for linear problems where the size of the observation vector is smaller than the size of the state vector (e.g., ATOVS). | |
|
Called by: IASI_Minimize |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Error_Report (2 times) IASI_Cholesky |
|
IASI_OpenFile Open a file for input/output using the next free unit number. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Initialise IASI_Read_Background IASI_Read_ControlData IASI_Read_Observations IASI_SetUpRetrievals RTIASI_Subroutines |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Error_Report (2 times) Gen_GetUnit Gen_MessageReport (2 times) |
|
IASI_ProcessData This is the main processing routine where each observation in turn is looped through and processed accordingly. The observation to be processed is first read in (an earlier version of this code had all the observations read in before this routine is called but memory considerations required this stage to be moved here - all the background data is still read in before this subroutine) and then the observation and background data are converted into the correct forms for the minimisation code to use. If required, the cloud detection step is performed next after which the channels to use are determined based on the cloud conditions and surface type. After the retrieval step itself (IASI_Minimize), the results output as required using the IASI_TranslateDataOut routine. | |
|
Called by: IASI_1DVar |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_Read_Observations Gen_Error_Report IASI_TranslateDataIn IASI_SetupBackground IASI_Fastmodel_Interface (2 times) IASI_CO2Slice IASI_CloudyOrNot IASI_Minimize IASI_TranslateDataOut Gen_MessageReport |
|
IASI_RMatrix_ChanSelect Picks out the selected channels from the observational error covariance matrix. (This is a little complicated for the band-diagonal representation of this matrix!) | |
|
Called by: IASI_CloudCost IASI_Minimize |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Error_Report (2 times) |
|
IASI_RTIASI_Interface This is the routine that interfaces with the RTIASI fast radiative transfer model (Matricardi and Saunders, 1999). It may be called in three different modes - initialise, direct and gradient. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Fastmodel_Interface |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_MessageReport RTIASI_RTTVI Gen_Error_Report (2 times) RTIASI_Direct RTIASI_K |
|
ASI_RTTOV7_Interface This is the routine that interfaces with the RTTOV7 fast radiative transfer model. It may be called in three different modes - initialise, direct and gradient. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Fastmodel_Interface |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_MessageReport (2 times) Gen_Error_Report (6 times) RTTVI CLEANUP RTTOV RTTOVK |
|
IASI_RTTOV8_Interface This is the routine that interfaces with the RTTOV8 fast radiative transfer model. It may be called in three different modes - initialise, direct and gradient. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Fastmodel_Interface |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_MessageReport (2 times) Gen_Error_Report (6 times) RTTOV_SETUP RTTOV_SETUPCHAN RTTOV_SETUPINDEX RTTOV_DIRECT RTTOV_K |
|
IASI_ReadHeaders Read in colon-separated fields in observation and background file headers. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Read_Background IASI_Read_Observations |
Calls (in order of first call): <NONE> |
|
IASI_Read_Background An example input routine for reading in the background profiles used in retrievals and placing the data in the BackGrModelOb structure (of ModelOb_Type derived type). This version reads from the file BACKGROUND.dat which is a formatted ASCII file. This routine expects the number of profiles in the input file to be either equal to the number of observations or to be one - in which case the same profile background is used for each observation. | |
|
Called by: IASI_1DVar_Driver |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_OpenFile (2 times) Gen_Error_Report (12 times) IASI_ReadHeaders (9 times) |
|
IASI_Read_ControlData Read in control data (from ControlData.NL). Details are in Section 3a. | |
|
Called by: IASI_1DVar_Driver |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_OpenFile Gen_Error_Report (7 times) |
|
IASI_Read_Observations An example input routine for reading in the observed radiances to be processed, plus auxiliary data, and placing the data in the Observations structure (of Ob_Type derived type). This version reads from the file ObsFile.dat which is a formatted ASCII file. The file also contains information on which of the channels belongs to which sub-instrument when a composite instrument (such as ATOVS) is being used. This version only reads one observation at a time (or none if all that is required is for the file to be opened and variables initialised) as the memory requirements are less than if all observations are read in at once. See Section 3c for more details. | |
|
Called by: IASI_1DVar_Driver IASI_ProcessData |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_OpenFile Gen_Error_Report (17 times) IASI_ReadHeaders (7 times) |
|
IASI_SatMatInv Uses Cholesky decomposition (Golub and Van Loan, 1996) to return the inverse of a symmetric positive definite matrix, A. If the the optional parameter Matrix is present, it is replaced by (Matrix).A-1 on exit and A is left u nchanged. If U is not positive definite this will be detected by the program and flagged as an error. U is assumed to be symmetric as only the upper triangle is in fact used. | |
|
Called by: IASI_CloudCost IASI_InitBmatrix IASI_Minimize IASI_Minimize_100 IASI_Minimize_100ML |
Calls (in order of first call): Gen_Error_Report (2 times) |
|
IASI_SetUpBackground Converts the background profile into a useable for for the minimisation code. Values are quality-controlled and the profiles may be flagged as invalid, modified (e.g., if supersaturated), or extrapolated (above model top, or to fill in data near the surface). Also the water vapour units are converted to those used in minimisation (Ln(kg/kg)) | |
|
Called by: IASI_ProcessData |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_StratosExtrap QSAT (2 times) |
|
IASI_SetUpRetrievals This reads in the variables to be retrieved from the Retrieval.NL namelist file as explained in Section 3b. | |
|
Called by: IASI_1DVar_Driver |
Calls (in order of first call): IASI_OpenFile Gen_Error_Report (6 times) |
|
IASI_StratosExtrap Code used to extrapolate the temperature above the model top (a very simple version is given here). This is only called when DoTExtrapolation is set to TRUE. in IASI_ProcessData . | |
|
Called by: IASI_SetUpBackground |
Calls (in order of first call): < NONE > |
|
IASI_TranslateDataIn Transform the input observation data into a form that can be better processed by the Fastmodel_Interface and the minimisation routines. If bias correction of the brightness temperatures is to be performed it should be done here. | |
|
Called by: IASI_ProcessData |
Calls (in order of first call): (User supplied bias correction scheme) |
|
IASI_TranslateDataOut Output results from processing. In an operational system, this subroutine would be used for converting the format of the output data into a form suitable for use in the next processing step. | |
|
Called by: IASI_ProcessData |
Calls (in order of first c
all): QSAT |
|
IASI_IntegerSort A sorting routine. | |
|
Called by: IASI_Channellist |
Calls (in order of first call): < NONE > |
|
QSAT A routine taken from the Met Office's Unified Model to return the water vapour saturation mixing ratio given pressure and temperature. | |
|
Called by: IASI_CheckIteration IASI_SetUpBackground IASI_TranslateDataOut |
Calls (in order of first call): < NONE > |
Golub, G.H. and C.F. Van Loan (1996). Matrix Computations. The Johns Hopkins University Press.